Advanced Coronal View Assessment
First Rib Inclination
The first rib articulates with the manubrium anteriorly and first thoracic vertebra posteriorly. It is a true rib and is the shortest and most curved of the ribs.
The scalene tubercle is on the superior surface between the grooves for the subclavian vessels. The scalenus anterior muscle attaches at this site.
Using a goniometer align the axis over C6-C7 junction and keep the stabilization arm level (using a bubble level will assist with this).
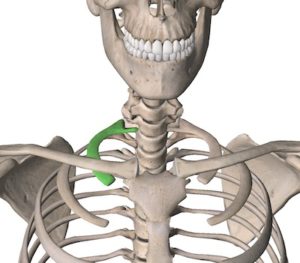
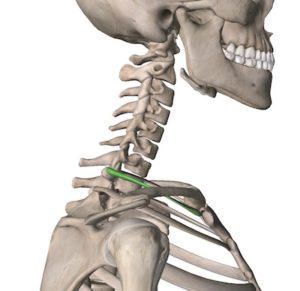
Align the movement arm over the superior surface of the manubrium of sternum.
An inclinometer (as shown in video) can also be used with the same landmarks.
- Using a goniometer align the axis over C6-C7 junction and keep the stabilization arm level (using a bubble level will assist with this).
- Align the movement arm over the superior surface of the manubrium of sternum.
- An inclinometer can also be used with the same landmarks.
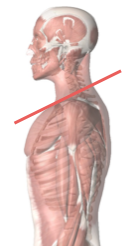
Normal inclination: 20-25 degrees
Pelvic Tilt
- Locate the PSIS and ASIS.
- Using a goniometer align the axis over the inferior surface of the PSIS and keep the stabilization arm level (using a bubble level will assist with this).
- Align the movement arm of the goniometer with the ASIS.
- Be sure to measure both sides to check for discrepancies that could be indicative of flexion disorder especially when leg length discrepancy is present.
- An inclinometer can also be used with the same landmarks.
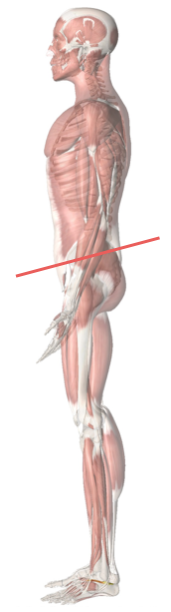
Extended Coronal Plane
- Malar surface
- Manubrium
- Pubic symphysis
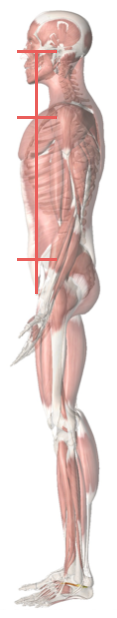
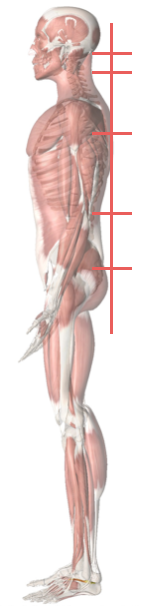
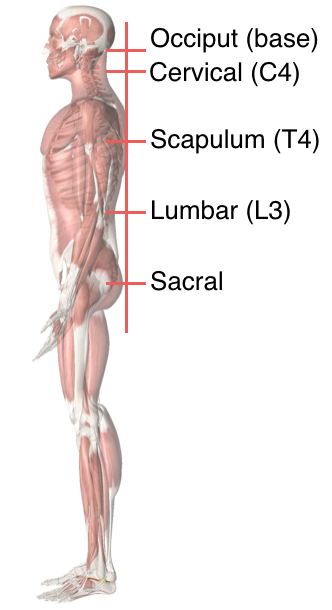
Spinal Coronal Plane
The sagittal plane gives us an indication regarding the vertical projection of the head in relationship to the pelvis and feet
In a balanced posture, resisting the pull of gravity has been shown to be optimal with the following postural landmarks .
- Occiput [2]
- Cervical (C4) [4]
- Thoracic (T5) [0]
- Lumbar (L3) [3]
- Sacral [0]
- Use the plumb line in your Postural Performance Assessment Tools
- Wrap the string around your index finger
- Point your index at the patient’s head
- Bring forward until the first point of contact.
There are 3 primary planes.
- Anterior Scapular Plane ASP
- Neutral Scapular Plane NSP
- Posterior Scapular Plane PSP
Anterior Scapular Plane (ASP)
Anterior Scapular Plane reduces availability to exploit the strength of the latissimus dorsi muscle as eccentric loading is limited
Sole of Biostimulation (SBS)
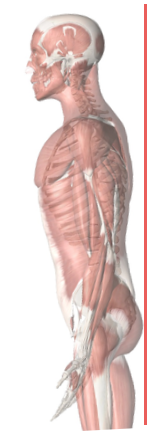
Neutral Scapular Plane (NSP)
Process of Postural Stabilization (PSP)
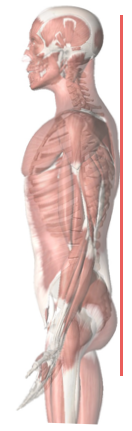
Posterior Scapular Plane (PSP)
Process of Postural Stabilization (PSP)