With the techniques that are presented here you will require the use of a goniometer to measure joint angles through a technique known as goniometry.
It is important that you achieve competency and proficiency in goniometric assessment to be able to achieve reliable assessment results.


Proper recording of goniometric measurements is a crucial aspect of the practice. Recordings should include enough information to properly document accurate interpretations of each measurement.
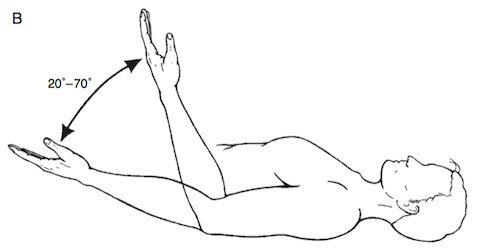
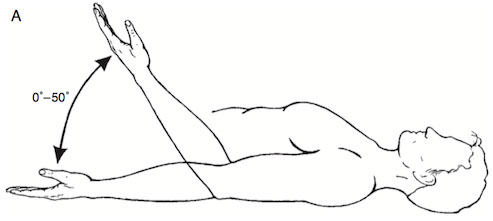
Recordings should include the starting and ending position in order to properly define the range of movement. For example, a bilateral comparison of elbow flexion is measured. On one side the range begins at 0° and ends at 50°, so the total range of movement is 50°.
This is recorded as 0 – 50°. If the client had 15° of hyperextension in the joint, it would be recorded as -15° – 0° – 50°. On the opposite arm, the motion starts at 20° and ends at 70°, so the total ROM is also 50°, but is recorded as 20° – 70°.
Testing Procedure
The testing procedure is initiated after the explanation has been given and the examiner is assured that the subject under- stands the nature of the testing process. The testing procedure consists of the following 12-step sequence of activities.
- Place the client in the testing position.
- Stabilize the proximal joint segment.
- Move the distal joint segment to the zero starting position. If the joint cannot be moved to the zero starting position, it should be moved as close as possible to the zero starting position. Slowly move the distal joint segment to the end of the passive ROM and determine the end-feel. Ask the client if there was any discomfort during the motion.
- Make a visual estimate of the ROM.
- Return the distal joint segment to the starting position. 6. Palpate the bony anatomical landmarks.
- Align the goniometer.
- Read and record the starting position. Remove the goniometer.
- Stabilize the proximal joint segment.
- Move the distal segment through the full ROM.
- Replace and realign the goniometer. Palpate theanatomical landmarks again if necessary.
- Read and record the ROM.
Recommendations for Improving the Reliability of Goniometric Measurements
- Use consistent, well-defined positions.
- Use consistent, well-defined, and carefully palpated anatomical landmarks to align the goniometer.
- Use the same amount of manual force to move client’s body part during successive measurements of passive ROM.
- Urge subject to exert the same effort to move the body part during successive measurements of active ROM.
- Use the same device to take successive measurements.
- Use a goniometer that is suitable in size to the joint being measured.
- If examiner is less experienced, record the mean of several measurements rather than a single measurement.
- Have the same examiner, rather than a different examiner, take successive measurements.
